SoilWater App Reference Library
Here you will find a range of documents, presentations and videos relating to the SoilWater App.
Evaluation of SWApp
Independent review of SWApp by Dr Ann Starasts 2018

Science behind SWApp
Published: "Environmental Modelling & Software 104 (2018) pp55-63"
Abstract: Rainfall is low and unreliable in much of Australia's dryland cropping areas, requiring well-informed crop management for optimising yield and profit. Growing-season rainfall is usually supplemented by soil water during fallow periods preceding a crop. While rainfall is conveniently measured, the difficulty of measuring a soil's plant available water (PAW, mm) has led to using simulation models for estimating PAW. Here we developed a smartphone application (app) that simulates soil water balance by accessing weather, soil and crop data from databases and on-farm records. Predictions of PAW using the Howleaky modelling engine were compared with field measurements. Validation of the simulation engine across sites in Australian cropping areas showed good agreement between simulated and measured PAW. Errors in model estimates are compared with variability found within small fields. We conclude that estimating PAW for paddocks using a simulation model built in a smartphone app is a reliable and adaptable technology.
Common questions - soil water
A collection of commonly asked questions from extension activities in the Queensland DPI (1980-2005).
Answers based on tillage and catchment studies over 25 years.
SoilWaterApp
A note describing SoilWaterApp
(GRDC updates early 2016)

SWApp for irrigators
SWApp provide support to irrigators:
• tracking soil water;
• estimating amount and timing of future irrigations;
• exploring irrigation strategies.
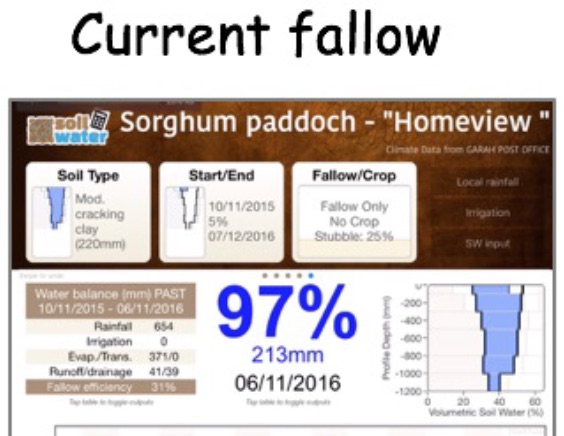
SWApp capability -dryland and irrigation
Brief note on applying SWApp in dryland and irrigation -four case studies
From Australian Cottongrower Dec 2016
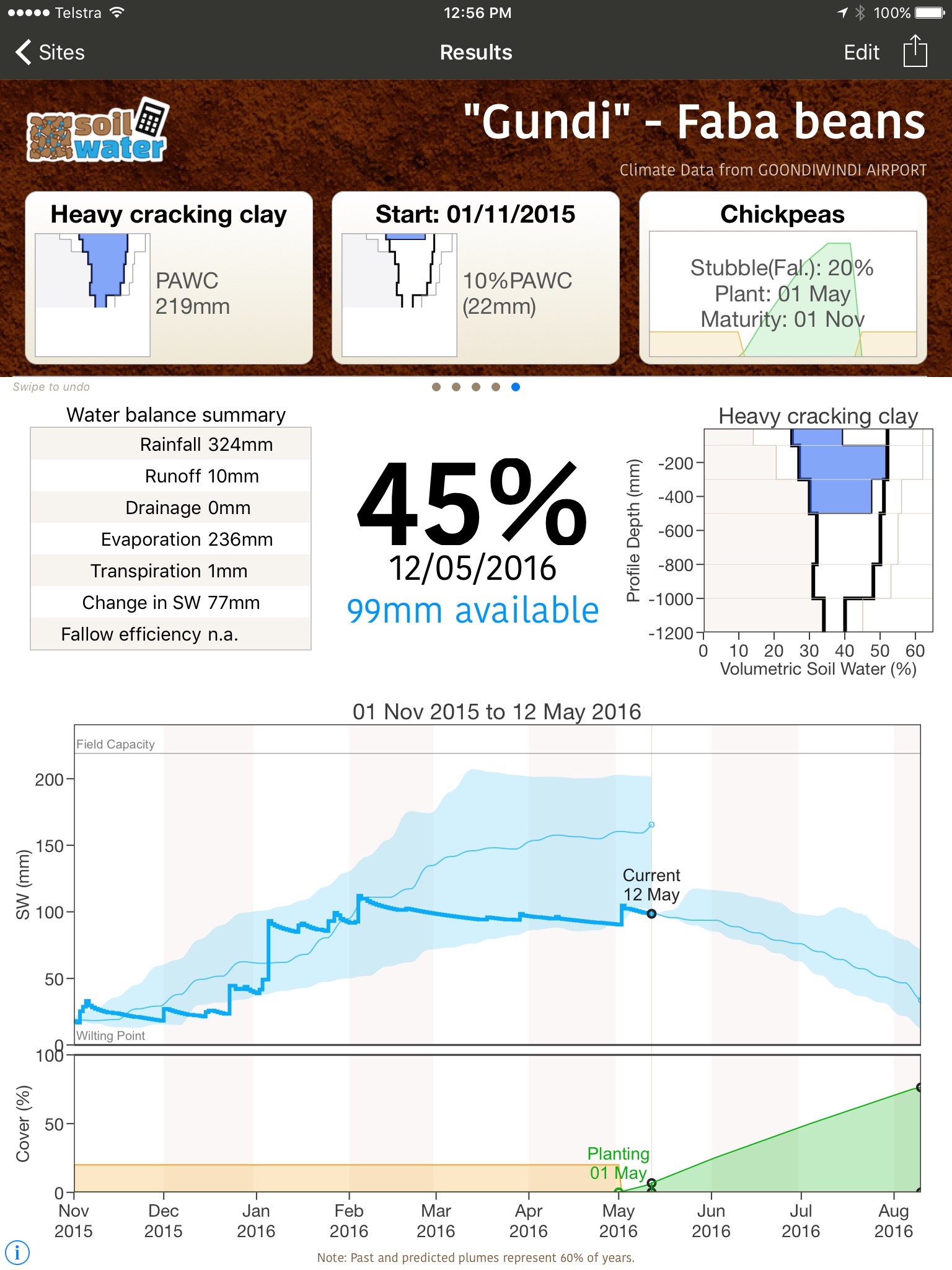
SoilWaterApp (PPT)
A PowerPoint presentation demonstrating SoilWaterApp functions
Apps in decision making
Application of two decision support tools (CliMate and SWApp) in decision making.
Presented at 18th Australian Cotton Conference Gold Coast 2016
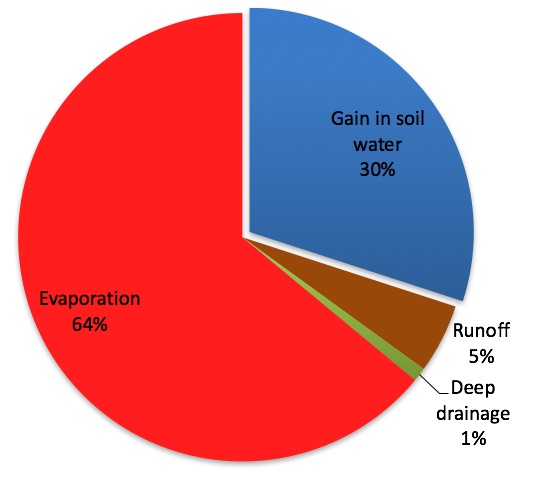
Soil water principles (PPT)
A PowerPoint presentation of soil water principles with examples mainly from the northern region.
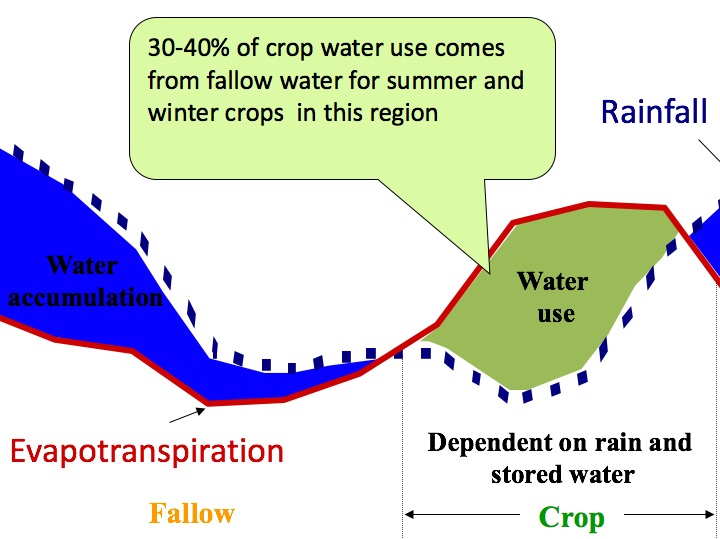
Soil water principles
A note describing principles of rainfall capture and storage.
Supported by experimental data, mainly from the northern grain growing region.

Soil water sensors
A review of devices for measuring soil moisture for use with the SoilWaterApp
Brett Robinson 2015
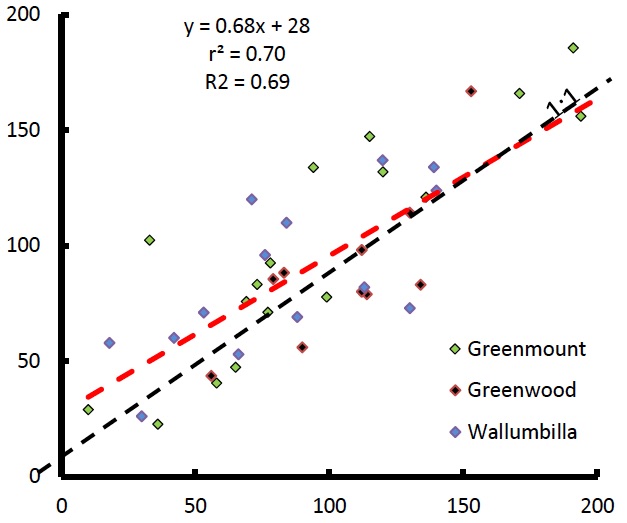
Testing SWApp (draft)
Detailed testing the water balance model on datasets from Queensland, Victoria and Western Australia.
SWApp predicts soil water well within the errors of measurements.
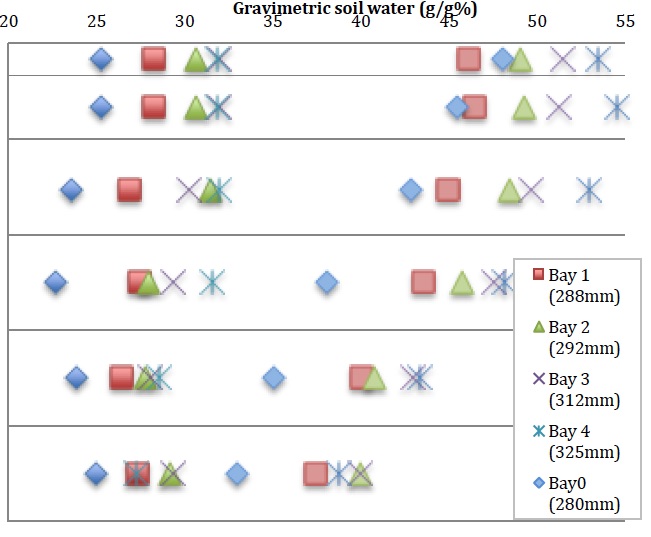
Field variability in soil water
An analysis of spatial and temporal variability in soil water and PAWC from three long term field studies
Conceptualisation and planning notes
Notes on the planning phase of SWApp including an analysis of where SWApp might fit in with other approaches and decision support tools
Monitoring soil water made easy
Documenting SWApp's ability to estimate soil water -Agronomy Conference 2017 Ballarat.
Testing SWApp (Conf. paper)
Testing SWApps ability to estimate change in soil water -Agronomy Confernce 2017 Ballarat

PERFECT (1989)
Model (v3) manual documenting water balance code used in Howleaky? and SoilWaterApp.